13 April, 2022
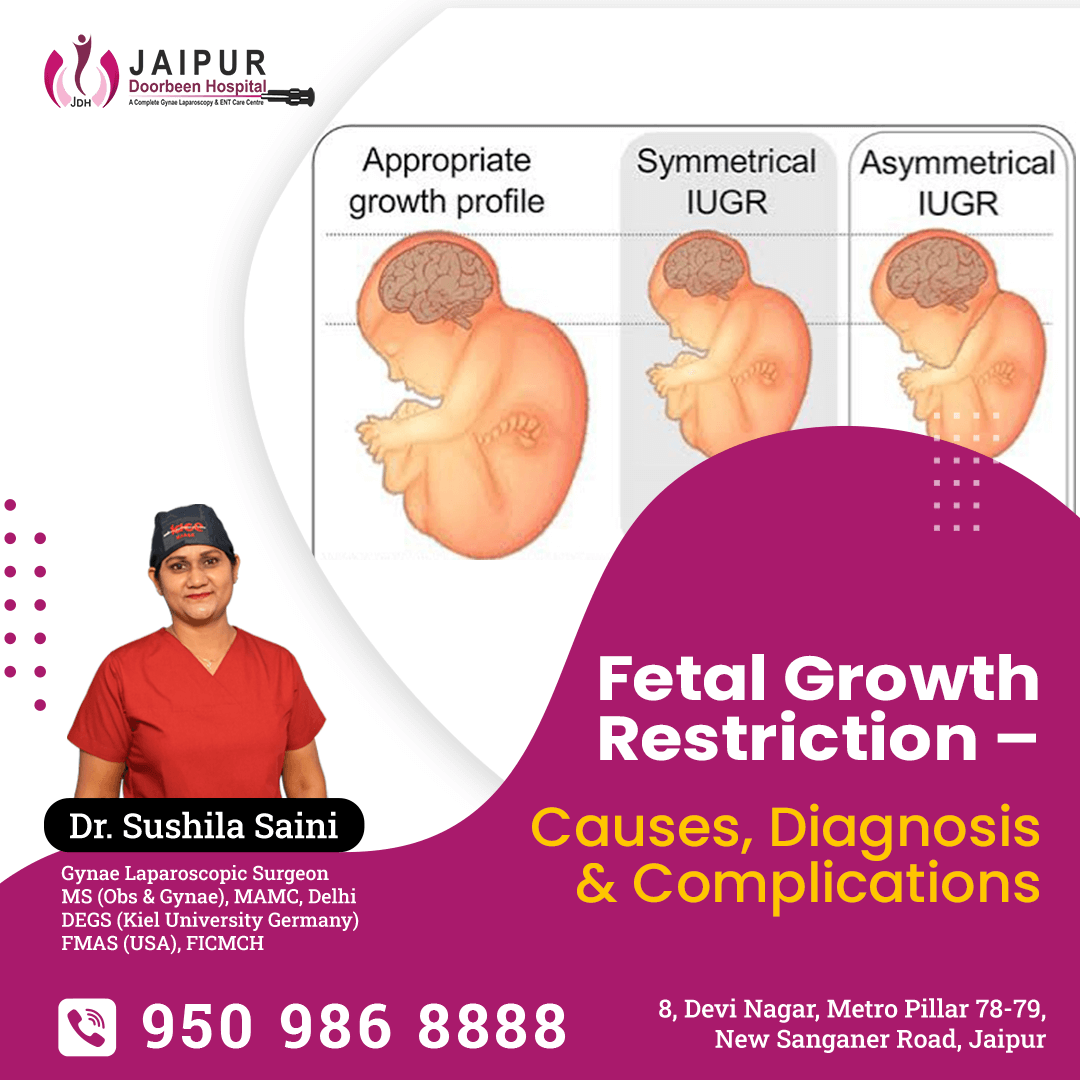
Fetal growth restriction is characterized by wherein the fetus does not achieve full intrauterine growth and development. FGR refers to a fetus with an EFW less than 10th percentile of the average for the gestational age on ultrasound.
Maternal causes-
• Constitutional
• Malnutrition
• Maternal disease- Anemia, hypertension, heart disease, chronic renal disease etc.
• Smoking, alcohol or any addiction
Fetal causes-
• Congenital anomalies either cardiovascular or renal or others
• Chromosomal abnormality
• Intrauterine infections
Placental causes-
• Placenta praevia, abruption etc.
Diagnosis:
• Your weight gain during pregnancy – remain stationary or at falling trends.
• Per abdominal examination done by your doctor by checking fundal height at your every ANC visit.
• Abdominal girth- remain stationary or at falling trends.
• Ultrasound for fetal well-being with color Doppler is confirmatory.
• Intra uterine death of fetus
• Still birth
• Fetal distress
• Meconium passage – It can leads to meconium aspiration syndrome.
• Other metabolic complications after birth
• Late complications- retarded neurologic & intellectual development, increase risk of development of cardiovascular disease ,type 2 diabetes etc. in their adulthood
Management – No definitive treatment has been demonstrated to be of benefit in growth restriction, assessment of fetal wellbeing and timely delivery remain the main management strategy.
• If mother is malnutrition- increase her total calories intake by increasing her diet, add high protein in diet like milk & milk products, pulses, egg, meat etc.
• Rest in left lateral position
• Quit alcohol, smoking or any drug addiction
• Fetal growth monitored by ultrasound according to severity of FGR.
• Plan time & mode of delivery accordingly.